LangChain - How to - Custom generator functions
2023. 10. 28. 04:08 |
https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/how_to/generators
Custom generator functions | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
You can use generator functions (ie. functions that use the yield keyword, and behave like iterators) in a LCEL pipeline.
python.langchain.com
Custom generator functions
You can use generator functions (ie. functions that use the yield keyword, and behave like iterators) in a LCEL pipeline.
LCEL 파이프라인에서 생성기 함수(즉, Yield 키워드를 사용하고 반복자처럼 동작하는 함수)를 사용할 수 있습니다.
The signature of these generators should be Iterator[Input] -> Iterator[Output]. Or for async generators: AsyncIterator[Input] -> AsyncIterator[Output].
이러한 생성기의 signature 은 Iterator[Input] -> Iterator[Output]이어야 합니다. 또는 비동기 생성기의 경우: AsyncIterator[Input] -> AsyncIterator[Output].
These are useful for: 이는 다음과 같은 경우에 유용합니다.
- implementing a custom output parser
- 사용자 정의 출력 파서 구현
- modifying the output of a previous step, while preserving streaming capabilities
- 스트리밍 기능을 유지하면서 이전 단계의 출력 수정
Let's implement a custom output parser for comma-separated lists.
쉼표로 구분된 목록에 대한 사용자 정의 출력 구문 분석기를 구현해 보겠습니다.
from typing import Iterator, List
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts.chat import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema.output_parser import StrOutputParser
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a comma-separated list of 5 animals similar to: {animal}"
)
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.0)
str_chain = prompt | model | StrOutputParser()
print(str_chain.invoke({"animal": "bear"}))이 코드는 ChatPromptTemplate, ChatOpenAI 모델 및 StrOutputParser를 사용하여 유사한 동물 5마리를 포함한 쉼표로 구분된 목록을 생성하는 예시를 제공합니다.
- ChatPromptTemplate 및 ChatOpenAI 모델 설정:
- ChatPromptTemplate.from_template()를 사용하여 대화 템플릿을 생성합니다.
- 이 템플릿은 사용자에게 "{animal}" 변수를 포함한 예시 동물 이름을 기반으로 유사한 동물 5마리를 나열하라는 지시를 포함합니다.
- ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.0)를 사용하여 ChatOpenAI 모델을 설정합니다. 온도(temperature)를 0.0으로 설정하여 모델의 출력을 더 일관된 형태로 만듭니다.
- StrOutputParser를 사용한 대화 체인 설정:
- prompt | model | StrOutputParser()는 대화 템플릿, 모델 및 StrOutputParser를 연결하여 문자열을 처리하는 대화 체인을 설정합니다.
- 대화 체인 호출:
- str_chain.invoke({"animal": "bear"})는 "str_chain" 대화 체인을 호출하고 "{animal}" 변수를 "bear"로 설정하여 질문을 수행합니다.
- 출력 결과:
- "print(str_chain.invoke({"animal": "bear"}))"는 대화 체인의 결과를 출력합니다.
이 코드는 ChatPromptTemplate, ChatOpenAI 모델 및 StrOutputParser를 사용하여 유사한 동물 목록을 생성하고 출력 결과를 확인하는 예시를 제공합니다.
lion, tiger, wolf, gorilla, panda
# This is a custom parser that splits an iterator of llm tokens
# into a list of strings separated by commas
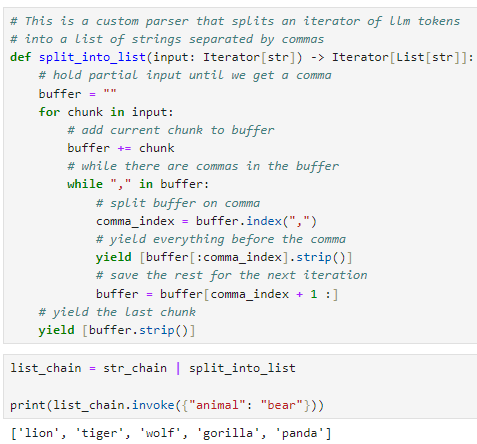
def split_into_list(input: Iterator[str]) -> Iterator[List[str]]:
# hold partial input until we get a comma
buffer = ""
for chunk in input:
# add current chunk to buffer
buffer += chunk
# while there are commas in the buffer
while "," in buffer:
# split buffer on comma
comma_index = buffer.index(",")
# yield everything before the comma
yield [buffer[:comma_index].strip()]
# save the rest for the next iteration
buffer = buffer[comma_index + 1 :]
# yield the last chunk
yield [buffer.strip()]list_chain = str_chain | split_into_list
print(list_chain.invoke({"animal": "bear"}))이 코드는 사용자 정의 파서를 정의하고, 이 파서를 사용하여 문자열을 쉼표로 구분된 목록으로 분할하는 예시를 제공합니다.
- split_into_list 함수 정의:
- split_into_list 함수는 입력으로 받는 input이라는 이터레이터를 받아, 이터레이터에서 가져온 LLM (Language Model) 토큰을 쉼표로 구분된 목록으로 분할하는 역할을 합니다.
- 함수 내부에 buffer라는 문자열을 사용하여 현재까지의 토큰을 임시로 저장합니다.
- for 루프를 사용하여 input에서 토큰을 하나씩 가져오고, buffer에 현재 토큰을 추가합니다.
- while 루프를 사용하여 buffer에서 쉼표가 있는지 확인하고, 쉼표가 있는 동안 다음 작업을 수행합니다.
- 쉼표를 기준으로 buffer를 분할하고, 쉼표 앞의 내용을 반환하고, 나머지 내용은 다음 반복을 위해 저장합니다.
- 마지막에 남은 내용을 반환합니다.
- str_chain과 split_into_list를 결합:
- str_chain은 이전 코드에서 설정한 대화 체인으로, 문자열을 생성하는 역할을 합니다.
- str_chain | split_into_list는 이전 체인에 split_into_list 파서를 추가하여 문자열을 쉼표로 구분된 목록으로 변환하는 새로운 대화 체인을 설정합니다.
- 대화 체인 호출:
- list_chain.invoke({"animal": "bear"})는 "list_chain" 대화 체인을 호출하고 "{animal}" 변수를 "bear"로 설정하여 질문을 수행합니다.
- 출력 결과:
- print(list_chain.invoke({"animal": "bear"}))는 대화 체인의 결과를 출력합니다. 이 결과는 쉼표로 구분된 동물 목록입니다.
이 코드는 사용자 정의 파서를 사용하여 문자열을 구문 분석하고 구분된 목록으로 변환하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
'LangChain > LangChain Expression Language' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LC - Cookbook - Multiple chains (0) | 2023.11.05 |
|---|---|
| LC - Cookbook - RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) (0) | 2023.11.05 |
| LC - Cookbook - Prompt + LLM (1) | 2023.10.29 |
| LangChain - How to - Route between multiple Runnables (1) | 2023.10.28 |
| LangChain - How to - Use RunnableParallel/RunnableMap (1) | 2023.10.28 |
| LangChain - How to - Run arbitrary functions (0) | 2023.10.28 |
| LangChain - How to - Add fallbacks (1) | 2023.10.28 |
| LangChain - How to - Configuration (0) | 2023.10.27 |
| LangChain - How to - Bind runtime args (0) | 2023.10.27 |
| LangChain - Interface (0) | 2023.10.27 |

